

Step 3: Look for potential outliers (see above image) Larger ranges indicate wider distribution, that is, more scattered data.

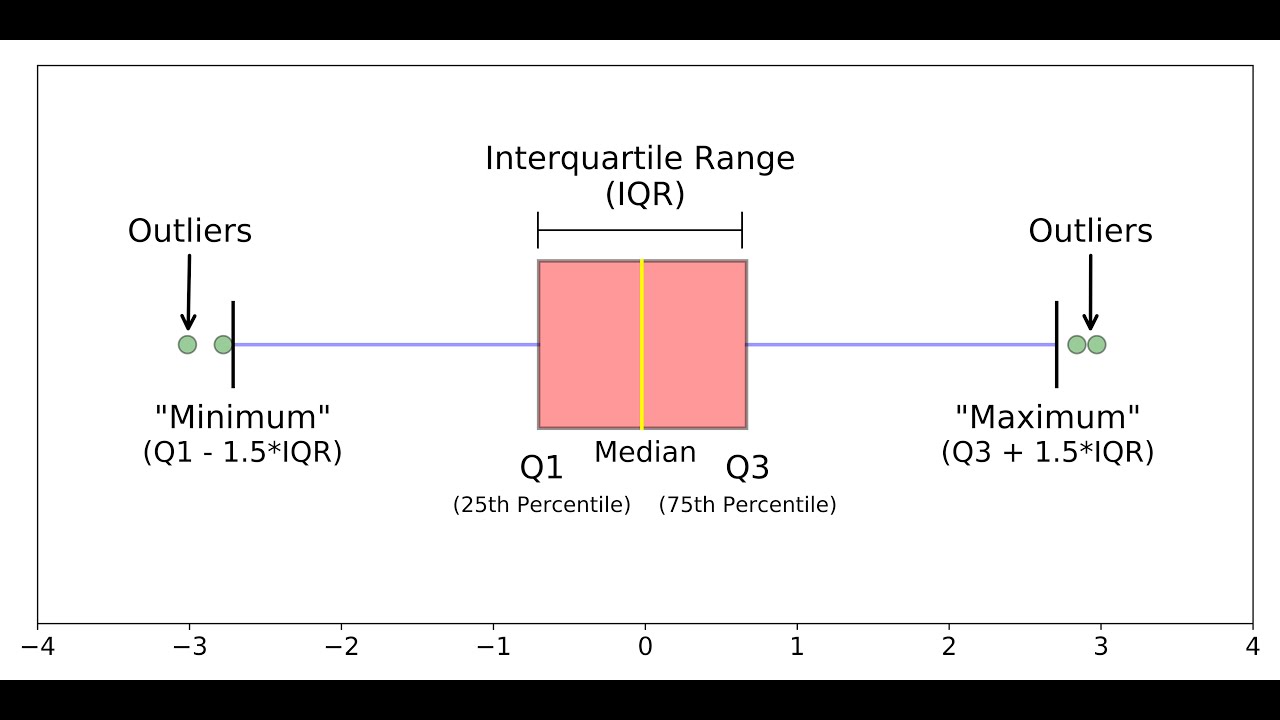
This shows the range of scores (another type of dispersion). Next, look at the overall spread as shown by the extreme values at the end of two whiskers. The longer the box the more dispersed the data. Step 2: Compare the interquartile ranges and whiskers of box plotsĬompare the interquartile ranges (that is, the box lengths), to examine how the data is dispersed between each sample. If the median line of a box plot lies outside of the box of a comparison box plot, then there is likely to be a difference between the two groups. Note, although box plots have been presented horizontally in this article, it is more common to view them vertically in research papersĬompare the respective medians of each box plot. This is the box plot showing the middle 50% of scores (i.e., the range between the the lower 25% of scores and the upper 25% of scores). The upper and lower whiskers represent scores outside the middle 50% (i.e. The highest score, excluding outliers (shown at the end of the right whisker). Seventy-five percent of the scores fall below the upper quartile value (also known as the third quartile). A box plot is constructed of two parts, a box and a set of whiskers as shown below. John Tukey, an American mathematician and statistician. Illustrated definition of Box and Whisker Plot: A special type of diagram showing Quartiles 1, 2 and 3 (where the data can be split into quarters) in a box, with. Half the scores are greater than or equal to this value and half are less. The box plot, also referred to as a box and whiskers plot, was introduced in 1970 by Dr. The median marks the mid-point of the data and is shown by the line that divides the box into two parts (sometimes known as the second quartile). Step 3: Subtract the number you found in step 1 from the number you found in step 3. Q1 is represented by the left hand edge of the box (at the point where the whisker stops).
Definition of box and whisker plot how to#
Twenty-five percent of scores fall below the lower quartile value (also known as the first quartile). Box Plot interquartile range: How to find it. The lowest score, excluding outliers (shown at the end of the left whisker). Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness through displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages.īox plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score. The name, box and whisker plot is derived from the nature. It may also have line extensions extending from the boxes, which usually indicates variability beyond the upper and lower quartiles. We use the VBOX or HBOX Statement in PROC SGPLOT and specify the analysis variable.In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as box and whisker plot) is a type of chart often used in explanatory data analysis. A box plot is a statistical data visualization technique that uses rectangular bars to indicate data groups through their quartiles. I have used the same data set as above in this article. The image above is a boxplot.A boxplot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five number summary (minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and maximum). First, let us look at a very simple example. Box and whisker plot Explanation & Examples. Interpreting box plots/Box plots in general. Whiskers often (but not always) stretch over a wider range of scores than the middle quartile groups. You can create a BOX Plot in SAS using the SG PLOT procedure. Whiskers The upper and lower whiskers represent scores outside the middle 50. Q1 – 1.5 * IQR How to create a Box and Whisker plot in SAS? Similarly, if a value is lower than the 1.5*IQR below the lower quartile (Q1), the value will be considered an outlier. Outlier: If a data point is higher than the 1.5*IQR above the upper quartile (Q3), the value will be considered an outlier. Interquartile range (IQR): It is the box plot showing the middle 50% of scores and can be calculated by subtracting the lower quartile from the upper quartile (e.g. A box-whisker plot is created using the default properties. Negatively Skewed: When the median is closer to the upper quartile (Q3) and the whisker is shorter on the upper end of the box, then the distribution is negatively skewed. Positively Skewed: When the median is closer to the lower or bottom quartile (Q1) then the distribution is positively skewed.
Normal Distribution or Symmetric Distribution: If a box plot has equal proportions around the median and the whiskers are the same on both sides of the box then the distribution is normal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
